ConfigCat Proxy
The ConfigCat Proxy allows you to host a feature flag evaluation service in your own infrastructure. It's a small Go application that communicates with ConfigCat's CDN network and caches/proxies config JSON files for your frontend and backend applications. The config JSON contains all the data that is needed for ConfigCat SDKs to evaluate feature flags.
The Proxy provides the following:
- Performance: The Proxy can be deployed close to your applications and can serve the downloaded config JSON files from memory. ConfigCat SDKs then can operate on the proxied config JSON. This can reduce the duration of feature flag evaluation for stateless or short lived applications.
- Reliability: The Proxy can store the downloaded config JSON files in an external cache. It can fall back to operating on the cached config JSON if the ConfigCat CDN network becomes inaccessible.
- Security: The Proxy can act as a server side flag evaluation component. Using it like that can prevent the exposure of config JSON files to frontend and mobile applications.
- Scalability: Horizontal scaling allows you to align with the load coming from your applications accordingly.
- Streaming: The Proxy provides real-time feature flag change notifications via Server-Sent Events (SSE) and gRPC.
Architecture
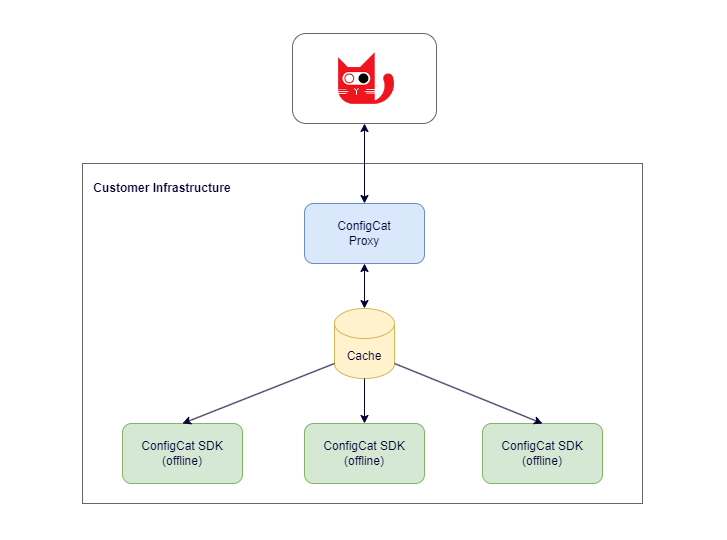
The following diagram shows the high level architecture of the Proxy.
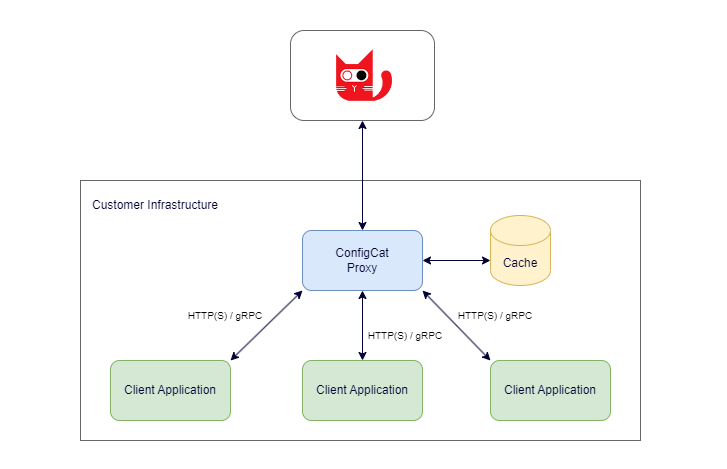
How It Works
The Proxy wraps one or more SDK instances for handling feature flag evaluation requests. It also serves the related config JSON files that can be consumed by other ConfigCat SDKs running in your applications.
Within the Proxy, the underlying SDK instances can run in the following modes:
- Online: In this mode, the underlying SDK has an active connection to the ConfigCat CDN network through the internet.
- Offline: In this mode, the underlying SDK doesn't have an active connection to ConfigCat. Instead, it uses the configured cache or a file as a source of its config JSON.
With the combination of the above modes, you can construct a cluster of proxies where only one node is responsible for the communication with ConfigCat, and all the other nodes are working from a central cache.
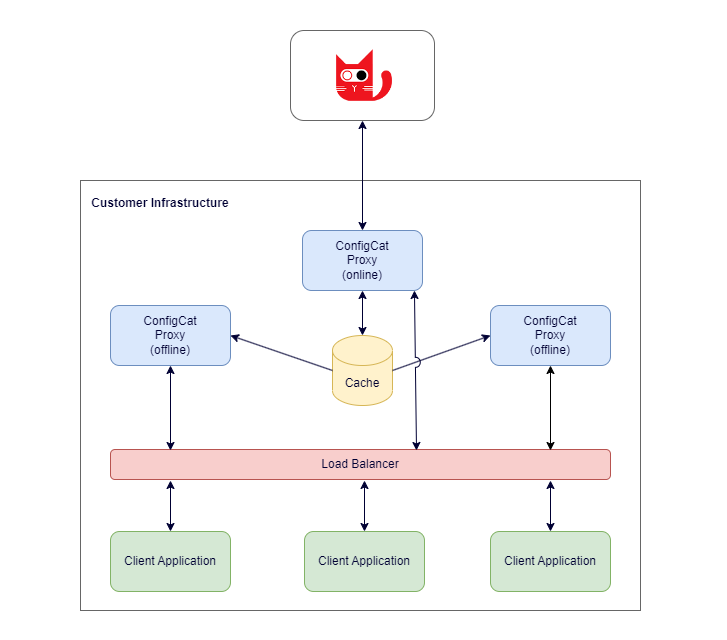
Communication
There are three ways how the Proxy is informed about the availability of new feature flag evaluation data:
- Polling: The ConfigCat SDKs within the Proxy are regularly polling the ConfigCat CDN for new config JSON versions.
- Webhook: The Proxy has webhook endpoints (for each underlying SDK) which can be set on the ConfigCat Dashboard to be invoked when someone saves & publishes new feature flag changes.
- Cache polling / file watching: In offline mode, the Proxy can regularly poll a cache or watch a file for new config JSON versions.
These are the ports used by the Proxy by default:
- 8050: for standard HTTP communication. (API, CDN proxy, Webhook, SSE)
- 8051: for providing diagnostic data (status, prometheus metrics).
- 50051: for gRPC communication.
Installation
You can install the ConfigCat Proxy from the following sources:
Docker
The docker image is available on DockerHub. You can run the image either as a standalone docker container or via docker-compose.
- Standalone
- docker-compose
Pull the docker image:
docker pull configcat/proxy
Run the ConfigCat Proxy:
docker run -d --name configcat-proxy \
-p 8050:8050 -p 8051:8051 -p 50051:50051 \
-e CONFIGCAT_SDKS='{"<sdk-identifier>":"<your-sdk-key>"}' \
configcat/proxy
services:
configcat_proxy:
image: configcat/proxy
environment:
- CONFIGCAT_SDKS={"<sdk-identifier>":"<your-sdk-key>"}
ports:
- "8050:8050"
- "8051:8051"
- "50051:50051"
To start docker services, execute the following command:
docker-compose up -f docker-compose.yml -d
Standalone executable
You can download the executables directly from GitHub Releases for your desired platform.
You can then check the status endpoint of the Proxy to ensure it's working correctly: http://localhost:8051/status
Usage Scenarios
This section describes the possible ways of how you can use the Proxy from your application. You can decide where you want the actual feature flag evaluation to happen.
- Local evaluation: Feature flags are evaluated by a ConfigCat SDK running in your application. The Proxy only provides the data required for the evaluation process.
- Remote evaluation: Feature flags are evaluated within the Proxy, your application only gets the result of the evaluation process.
1. Local evaluation using a ConfigCat SDK connected to the Proxy
The Proxy has the ability to forward all information required for feature flag evaluation to ConfigCat SDKs via its CDN proxy endpoint. This means that you can set up your ConfigCat SDK instances to use the Proxy as their data source.
To do this, you have to set the SDK's baseUrl option to the Proxy's host.
import * as configcat from "@configcat/sdk";
const configCatClient = configcat.getClient(
"#YOUR-SDK-KEY#",
configcat.PollingMode.AutoPoll,
{ baseUrl: "http://localhost:8050" } // Proxy URL
);
Additionally, as the Proxy maps unique identifiers to each configured SDK key it works with,
you can use that identifier prefixed with configcat-proxy/ as the SDK key at the ConfigCat SDK's initialization.
import * as configcat from "@configcat/sdk";
var configCatClient = configcat.getClient(
"configcat-proxy/#SDK-IDENTIFIER#", // SDK identifier prefixed with 'configcat-proxy/'
configcat.PollingMode.AutoPoll,
{ baseUrl: "http://localhost:8050" } // Proxy URL
);
2. Remote evaluation with the Proxy's API endpoints
You can leverage the Proxy's server side feature flag evaluation feature by sending simple HTTP requests to the Proxy's API endpoints.
const url = "http://localhost:8050/api/eval"; // Proxy API URL with SDK identifier
const data = {
key: "isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled", // Feature flag key
user: { // User Object for evaluation
Identifier: "#UNIQUE-USER-IDENTIFIER#"
}
};
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"X-ConfigCat-SdkKey": "#YOUR-SDK-KEY#",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(data),
};
try {
const response = await fetch(url, requestOptions);
const responseData = await response.json();
console.log(responseData); // {"value":<evaluated-value>,"variationId":"<variation-id>"}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error)
}
Additionally, as the Proxy maps unique identifiers to each configured SDK key it works with, you can use that identifier in the API endpoint's path instead of the SDK key header.
const url = "http://localhost:8050/api/#SDK-IDENTIFIER#/eval"; // Proxy API URL
const data = {
key: "isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled", // Feature flag key
user: { // User Object for evaluation
Identifier: "#UNIQUE-USER-IDENTIFIER#"
}
};
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(data),
};
try {
const response = await fetch(url, requestOptions);
const responseData = await response.json();
console.log(responseData); // {"value":<evaluated-value>,"variationId":"<variation-id>"}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error)
}
You can find the available API endpoints with their HTTP request/response schemas here.
3. Remote evaluation with OpenFeature Remote Evaluation Protocol (OFREP)
OFREP compatibility is only available from Proxy version v2.0.0.
The OFREP feature of the Proxy is turned OFF by default, to use it, you have to turn it ON with the OFREP endpoint options.
The Proxy conforms to the OpenFeature Remote Evaluation Protocol, which means it can be used with OFREP compatible OpenFeature providers.
import { OpenFeature } from "@openfeature/web-sdk";
import { OFREPWebProvider } from '@openfeature/ofrep-web-provider';
OpenFeature.setProvider(
new OFREPWebProvider({
baseUrl: "http://localhost:8050", // Proxy URL
headers: [
["X-ConfigCat-SdkKey", "#YOUR-SDK-KEY#"],
],
}),
);
Additionally, as the Proxy maps unique identifiers to each configured SDK key it works with,
you can use that identifier in the X-ConfigCat-SdkId HTTP header.
import { OpenFeature } from "@openfeature/web-sdk";
import { OFREPWebProvider } from "@openfeature/ofrep-web-provider";
OpenFeature.setProvider(
new OFREPWebProvider({
baseUrl: "http://localhost:8050", // Proxy URL
headers: [
["X-ConfigCat-SdkId", "#SDK-IDENTIFIER#"],
],
}),
);
You can find the available OFREP endpoints with their HTTP request/response schemas here.
4. Remote evaluation and streaming with SSE
The Proxy has the ability to evaluate feature flags and send notifications about subsequent evaluated flag value changes through Server-Sent Events connections.
const rawData = {
sdkKey: "#YOUR-SDK-KEY#",
key: "isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled", // Feature flag key
user: { // User Object for evaluation
Identifier: "#UNIQUE-USER-IDENTIFIER#"
}
}
const data = btoa(JSON.stringify(rawData))
const url = "http://localhost:8050/sse/eval/k"; // Proxy SSE URL
const evtSource = new EventSource(url + "/" + data);
evtSource.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log(event.data); // {"value":<evaluated-value>,"variationId":"<variation-id>"}
};
Additionally, as the Proxy maps unique identifiers to each configured SDK key it works with, you can use that identifier in the SSE endpoint's path.
const rawData = {
key: "isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled", // Feature flag key
user: { // User Object for evaluation
Identifier: "#UNIQUE-USER-IDENTIFIER#"
}
}
const data = btoa(JSON.stringify(rawData))
const url = "http://localhost:8050/sse/#SDK-IDENTIFIER#/eval"; // Proxy SSE URL with SDK identifier
const evtSource = new EventSource(url + "/" + data);
evtSource.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log(event.data); // {"value":<evaluated-value>,"variationId":"<variation-id>"}
};
For more information and usage examples, see the related SSE endpoints documentation.
5. Remote evaluation and streaming with gRPC
The Proxy supports both unary feature flag evaluation RPCs and server streaming of evaluated flag value changes. For more information and usage examples, see the gRPC section of this documentation.
Configuration Options
You can specify options for the Proxy either via a YAML file or with environment variables. When an option is defined in both places, the environment variable's value takes precedence.
By default, the Proxy reads the options YAML from the following default locations:
- Windows:
%PROGRAMDATA%\configcat\proxy\options.yml, usuallyC:\ProgramData\configcat\proxy\options.yml - macOS:
/Library/Application Support/configcat/proxy/options.yml - Linux:
/etc/configcat/proxy/options.yml
When the default location is not suitable, you can specify a custom location for your options YAML file via the -c argument.
- YAML
- Environment variables
Docker
When running the Proxy in docker, you can mount the options YAML file as a volume.
docker run -d --name configcat-proxy \
-p 8050:8050 -p 8051:8051 -p 50051:50051 \
-v <path-to-file>/options.yml:/etc/configcat/proxy/options.yml
(Optional) With the -c argument to specify a custom path for your options YAML file:
docker run -d --name configcat-proxy \
-p 8050:8050 -p 8051:8051 -p 50051:50051 \
-v <path-to-file>/options.yml:/cnf/options.yml \
configcat/proxy -c /cnf/options.yml
Standalone executable
Run the Proxy as a standalone executable with the options YAML file in its default location:
- macOS / Linux
- Windows
./configcat-proxy
.\configcat-proxy.exe
(Optional) With the -c argument to specify a custom path for your options YAML file:
- macOS / Linux
- Windows
./configcat-proxy -c /path-to-file/options.yml
.\configcat-proxy.exe -c \path-to-file\options.yml
Docker
When running the Proxy in docker, you can pass environment variables to the executing container.
docker run -d --name configcat-proxy \
-p 8050:8050 -p 8051:8051 -p 50051:50051 \
-e CONFIGCAT_SDKS='{"<sdk-identifier>":"<your-sdk-key>"}' \
configcat/proxy
Standalone executable
Make sure the related environment variables are available for the Proxy's hosting process.
- shell
- PowerShell
export CONFIGCAT_SDKS='{"<sdk-identifier>":"<your-sdk-key>"}'
Then start the Proxy:
./configcat-proxy
$Env:CONFIGCAT_SDKS='{"<sdk-identifier>":"<your-sdk-key>"}'
Then start the Proxy:
.\configcat-proxy.exe
The following sections will go through each available option in detail.
How does the Proxy learn about feature flags?
In order to make the Proxy work properly, it must be set up with one or more SDK keys. It creates one SDK instance per SDK key internally and uses those for feature flag evaluation.
SDK Identifier
Within the Proxy, SDK keys are mapped to unique SDK identifiers.
The SDK key identifies a config-environment pair and is used to configure an SDK instance to fetch the config JSON of that config-environment pair. The SDK identifier identifies an SDK instance running within the Proxy and configured to use the associated SDK key. That is, the SDK identifier is effectively an alias for the associated SDK key and is used in endpoint routes to avoid exposing the SDK Key.
There are two ways to let the Proxy know which SDK Keys it should use:
1. Automatic configuration with Proxy profiles
Beta Feature: Automatic configuration with Proxy profiles is in public beta. We're now collecting feedback from real-world usage to fine-tune the experience. Share your feedback here.
The automatic configuration with Proxy profiles feature is only available from Proxy version v2.0.0.
The Proxy has the ability to use Proxy profiles to determine which SDK keys to download and distribute. It periodically checks for profile changes, allowing it to pick up the changes on the fly, without needing a restart.
By using Proxy profiles, your deployed Proxy instances can detect and react to:
- SDK key rotation.
- Data governance change.
- Product, config and environment state changes, such as creation, renaming and deletion.
You can set up Proxy profiles under the Manage organization -> Proxy Profiles menu on the ConfigCat Dashboard.
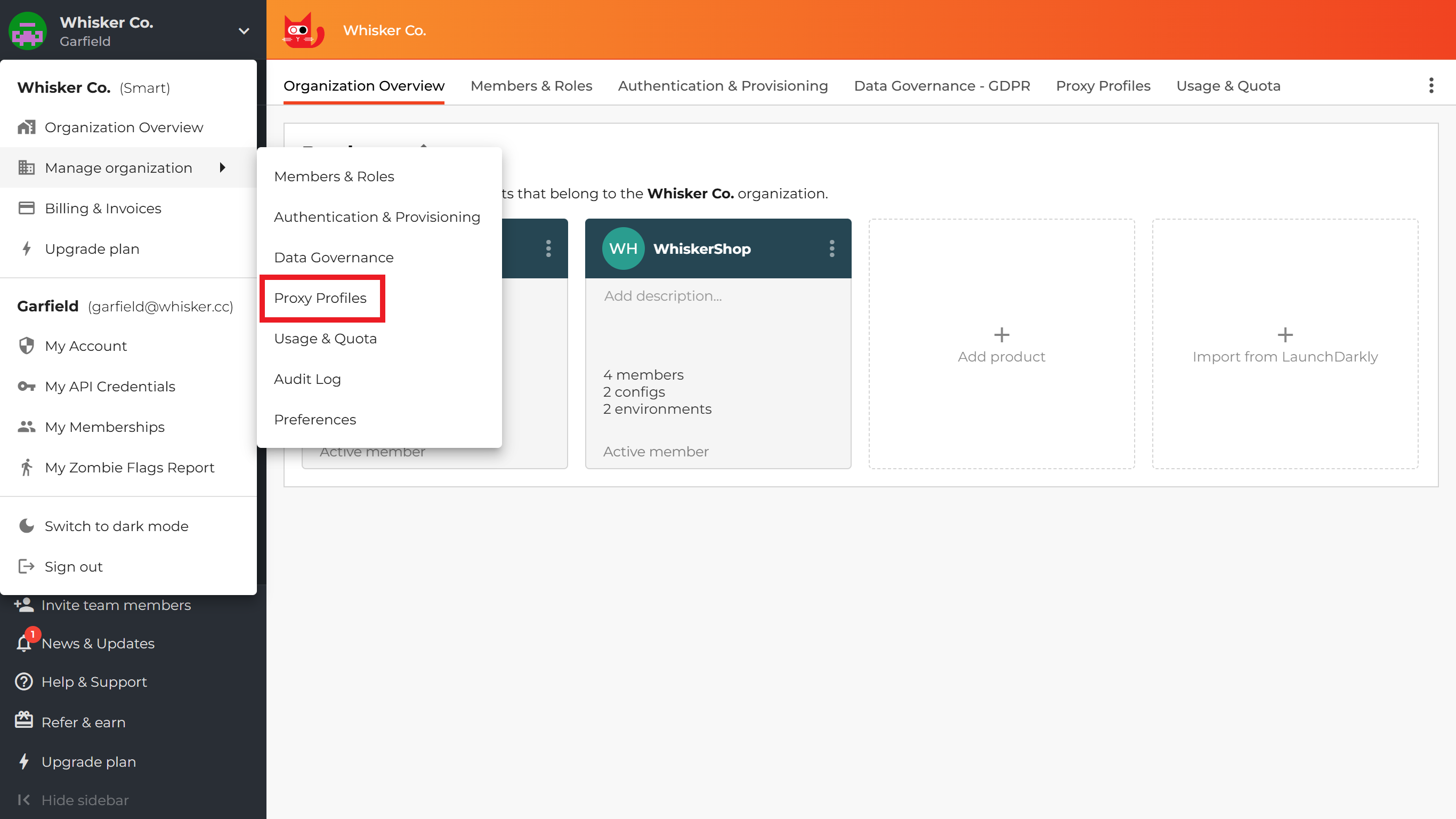
To connect a Proxy instance to a Proxy profile, follow these steps:
-
Create a new Proxy profile
Click on the
+ ADD PROFILEbutton.
Give the profile a meaningful name and description, then click
CREATE.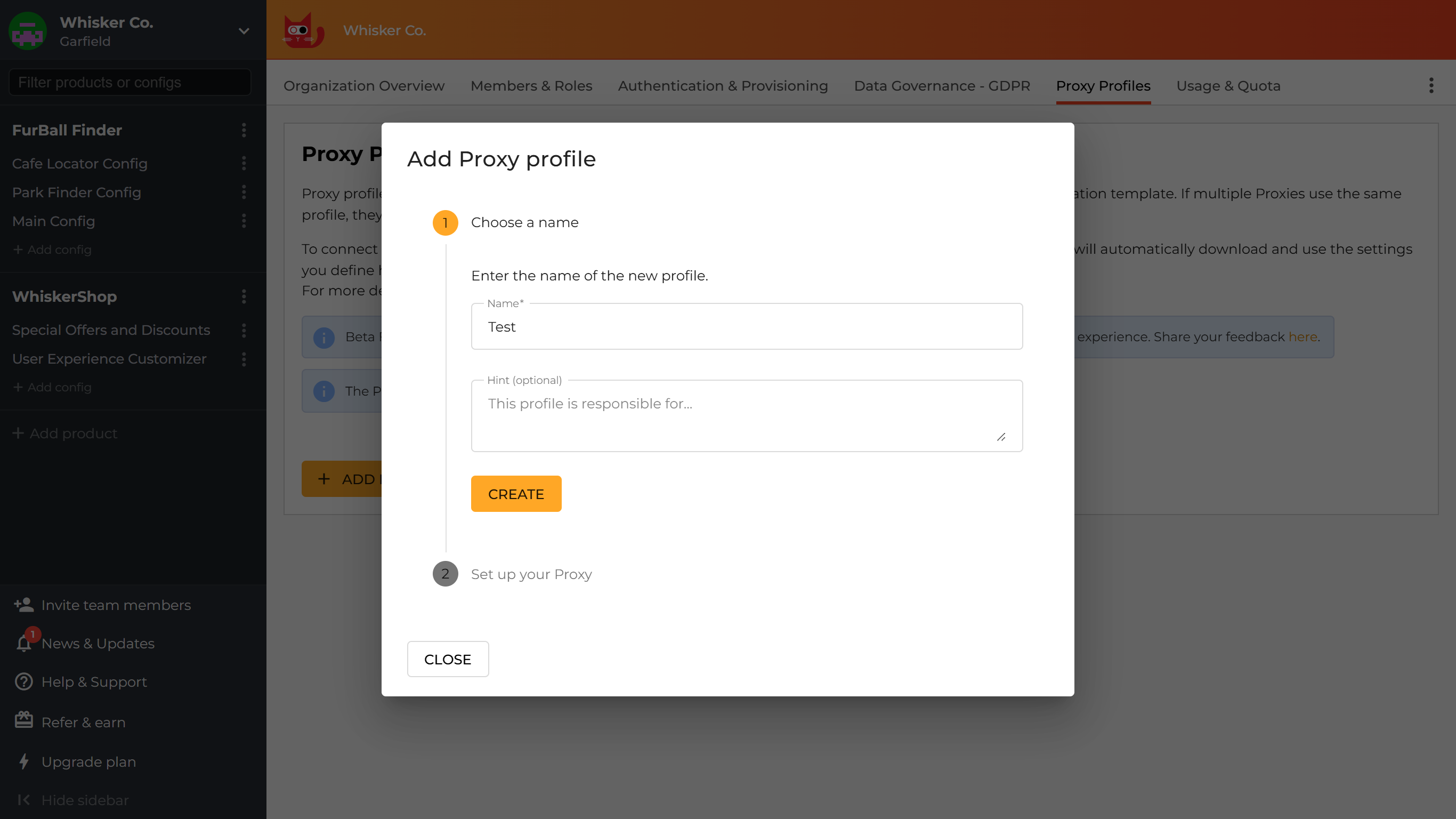
-
Configure your Proxy instance
Grab the
KeyandSecretfrom the profile creation dialog and put them into the Proxy's configuration.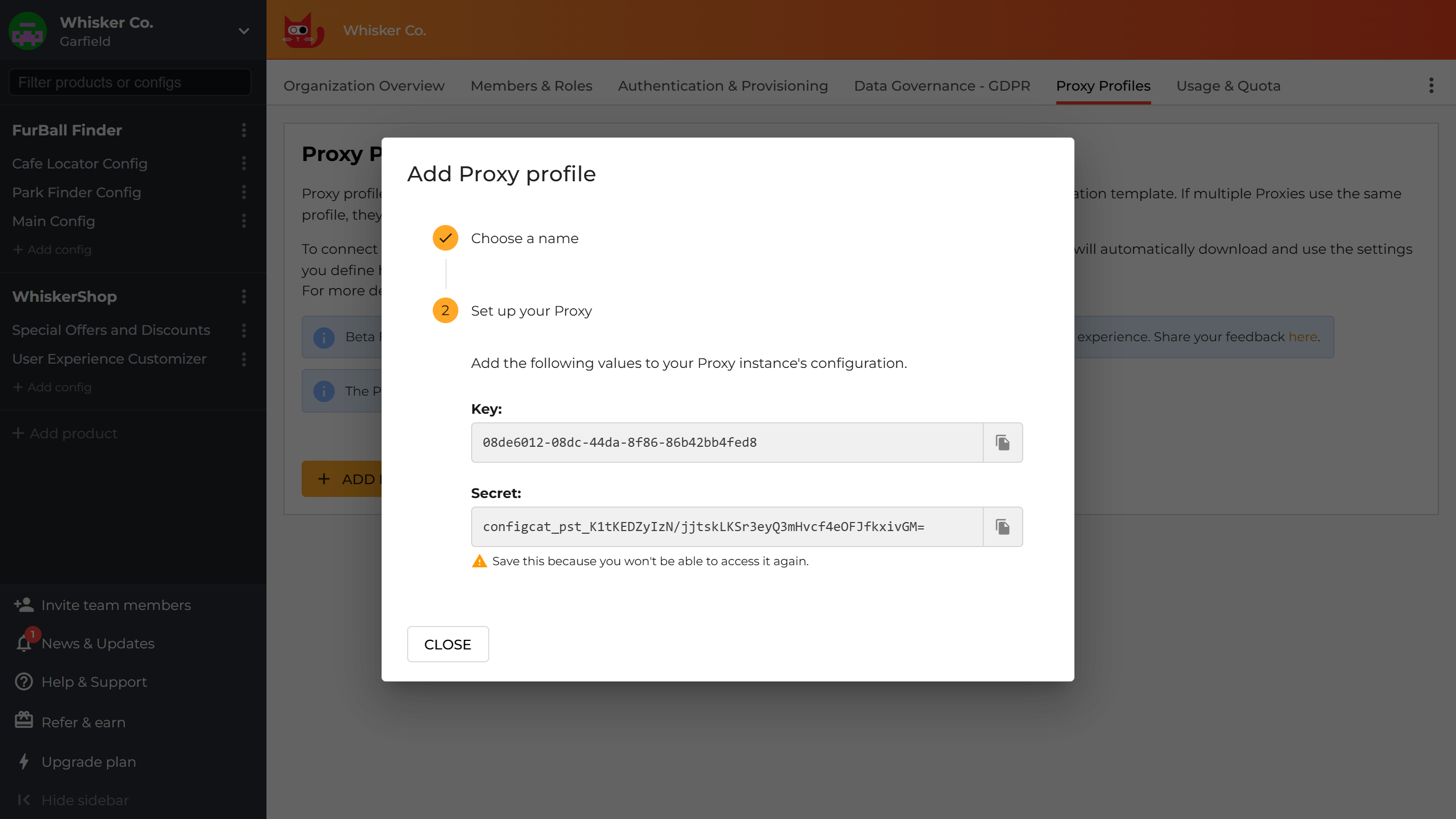
- YAML
- Environment variables
options.ymlprofile:
key: <key>
secret: <secret>CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_KEY="<key>"
CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_SECRET="<secret>"
-
Select which SDK Keys your Proxy should use
Click on the edit icon in the
SDK Keyscolumn.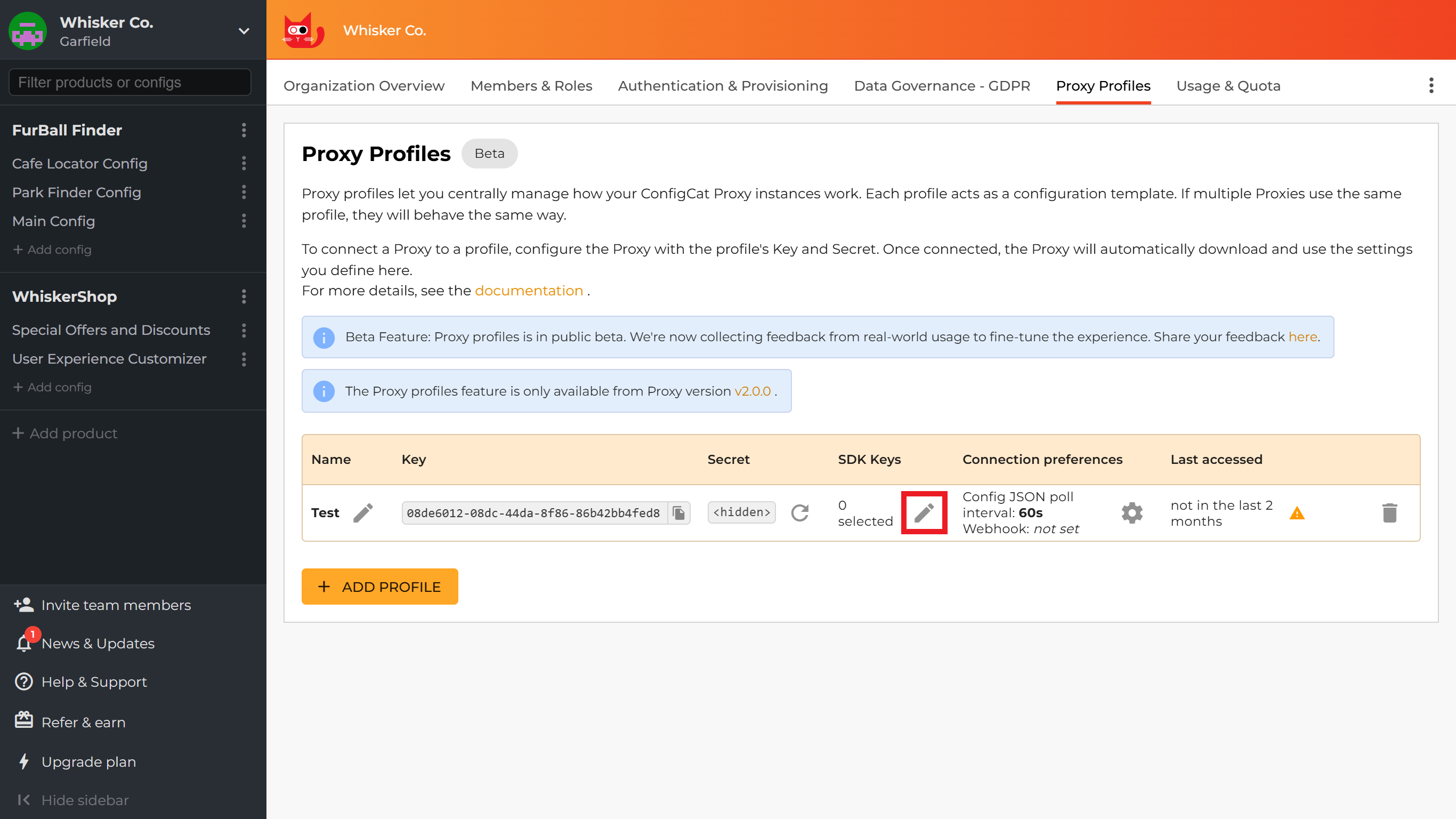
You can choose SDK Keys in two ways: by creating selection rules or by choosing individual SDK Keys manually. Your applications will have access to all feature flags in the config-environment pairs whose SDK Keys you select.
-
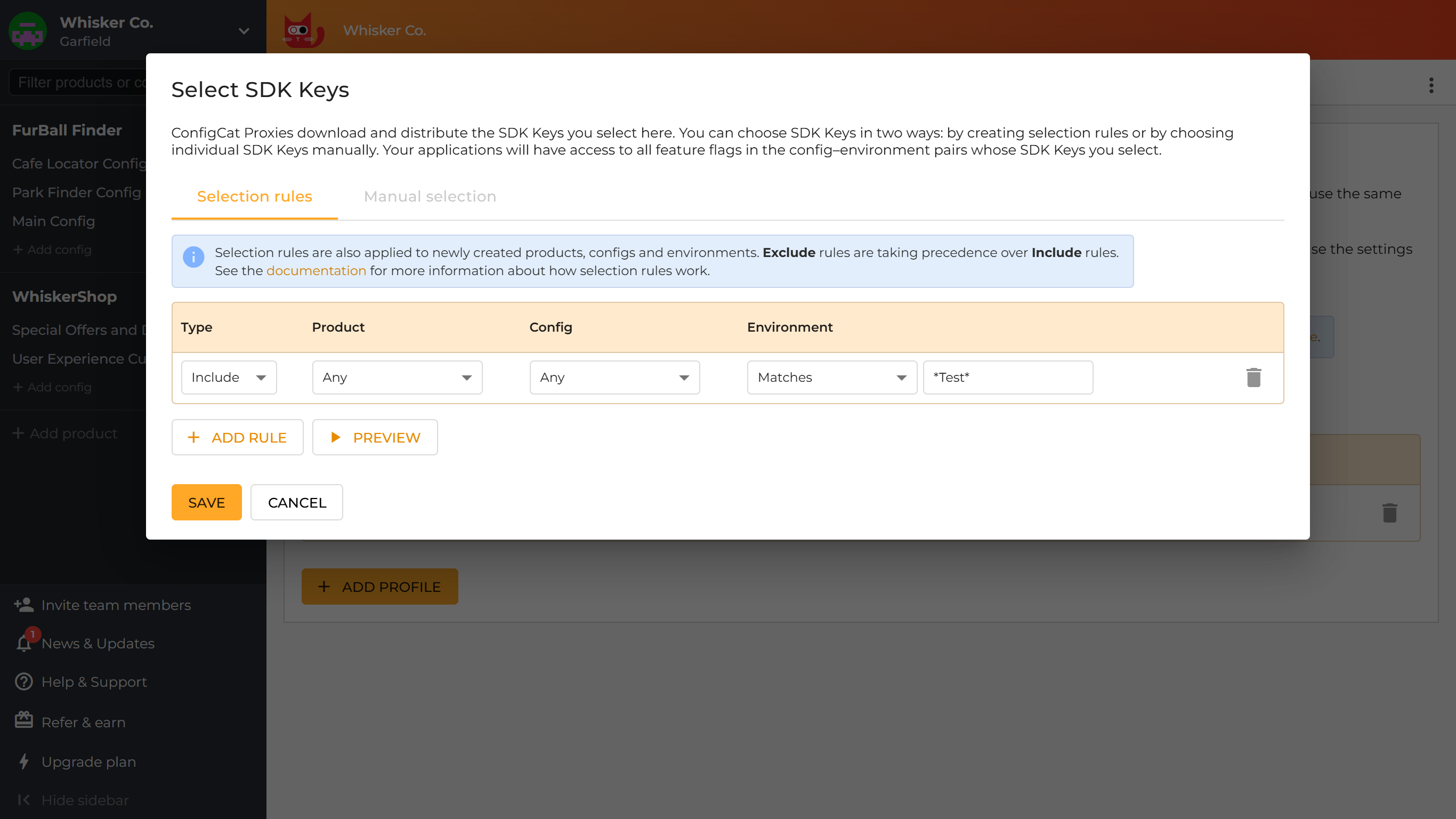
Selection rules
With selection rules, you can describe which existing and future config-environment pairs should be distributed to Proxy instances. Rules can be based on products, configs and environments with the following filtering options:
- Exact (by selecting an exact product, config or environment): This option filters for the ID of the selected product, config or environment. It's not sensitive to renaming.
- Any: This option is similar to a single wildcard (
*) expression. It filters for every product, config or environment. - Match expression (by selecting
Matches): This option matches the given pattern to the name of products/configs/environments, accepting wildcards (*). It's sensitive to renaming.
Whenever a config-environment pair matches both an Include and an Exclude rule, the Exclude rule will always take precedence.
-
Manual selection
You can manually select the config-environment pairs whose SDK key you want to make available for your Proxy instance.
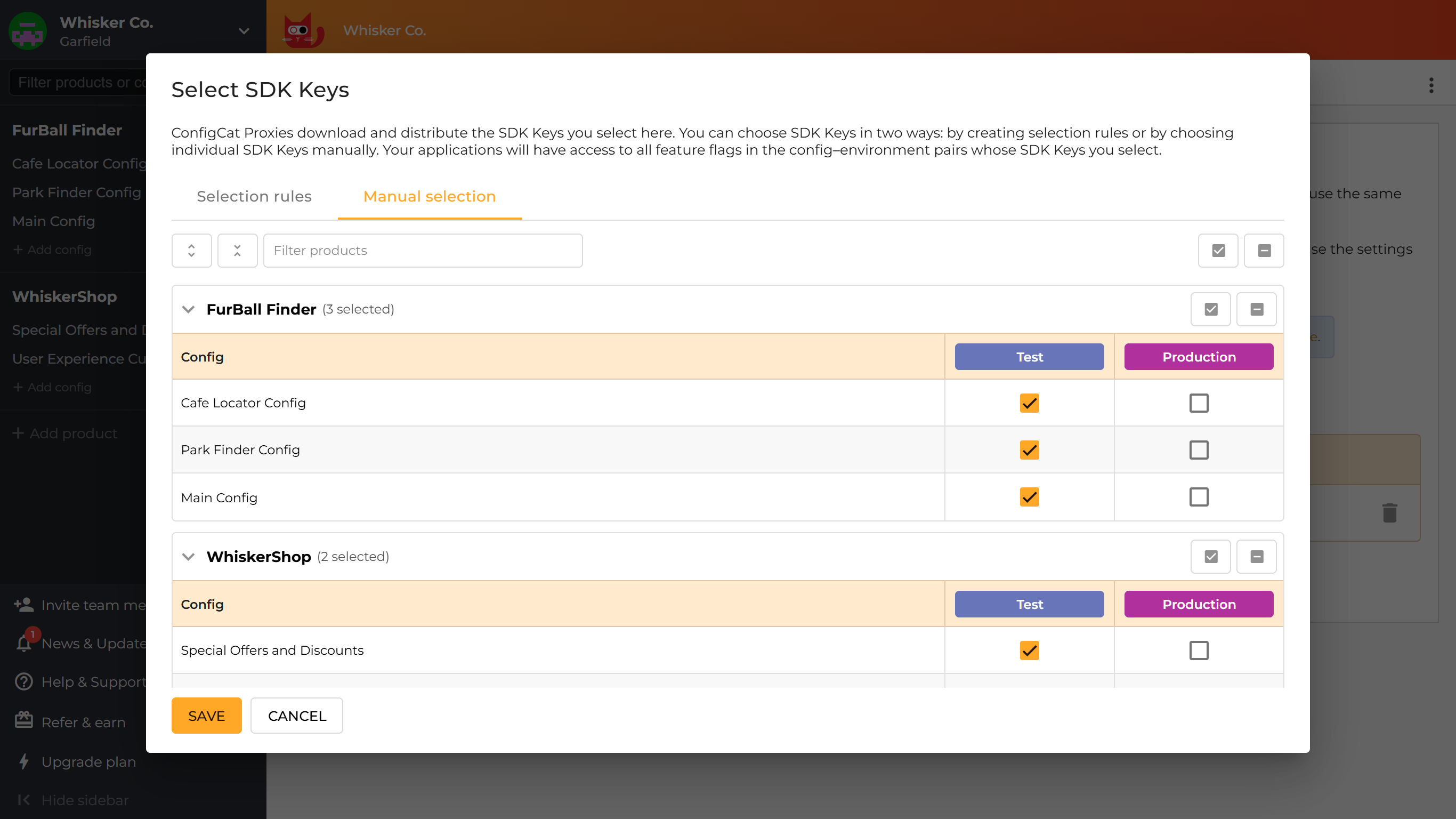 info
infoYou can click config names in the first column to toggle all SDK keys in a row, or environment names in the column headers to toggle all SDK keys in a column.
-
-
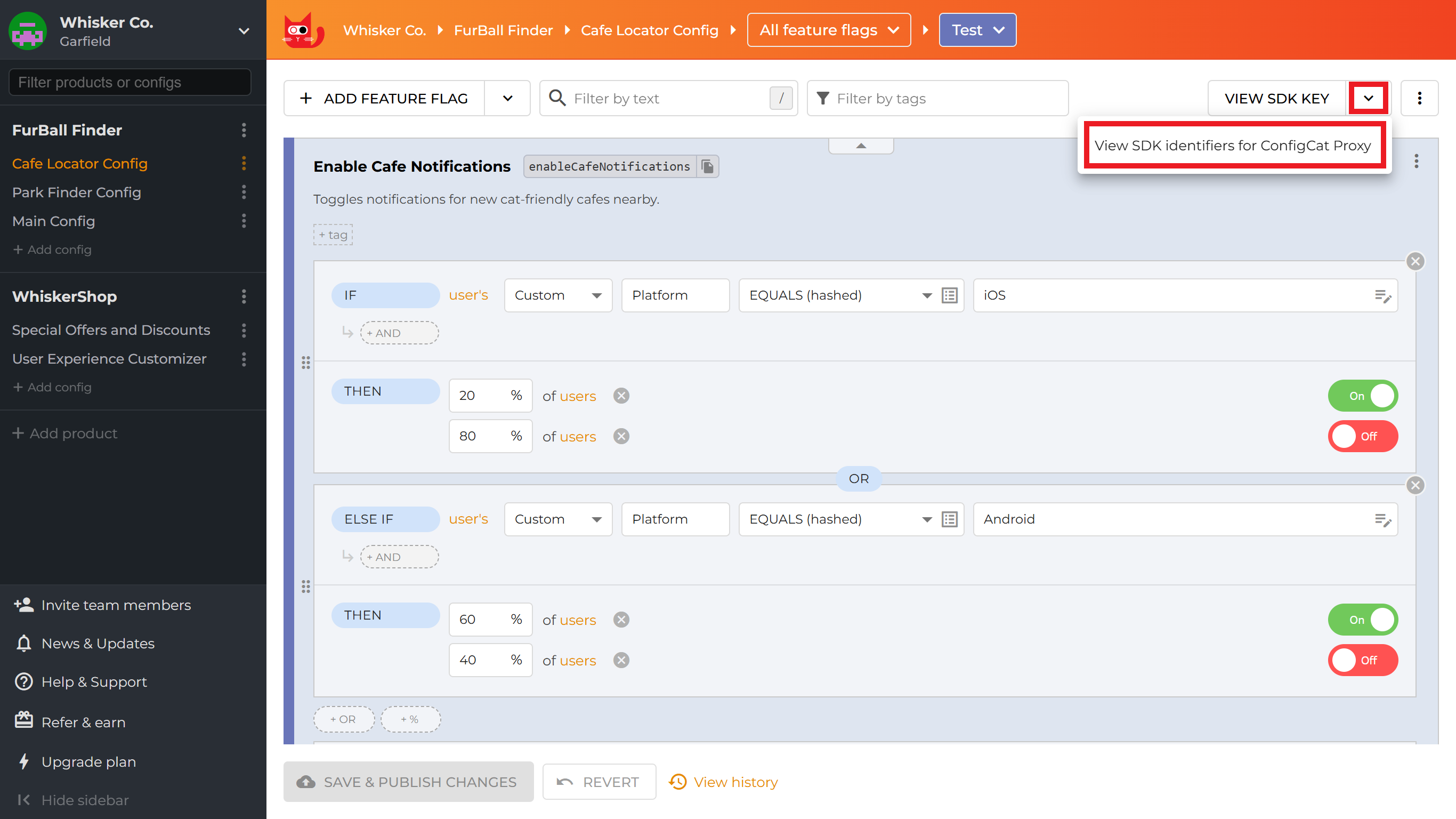
Locate SDK identifiers for the selected SDK Keys
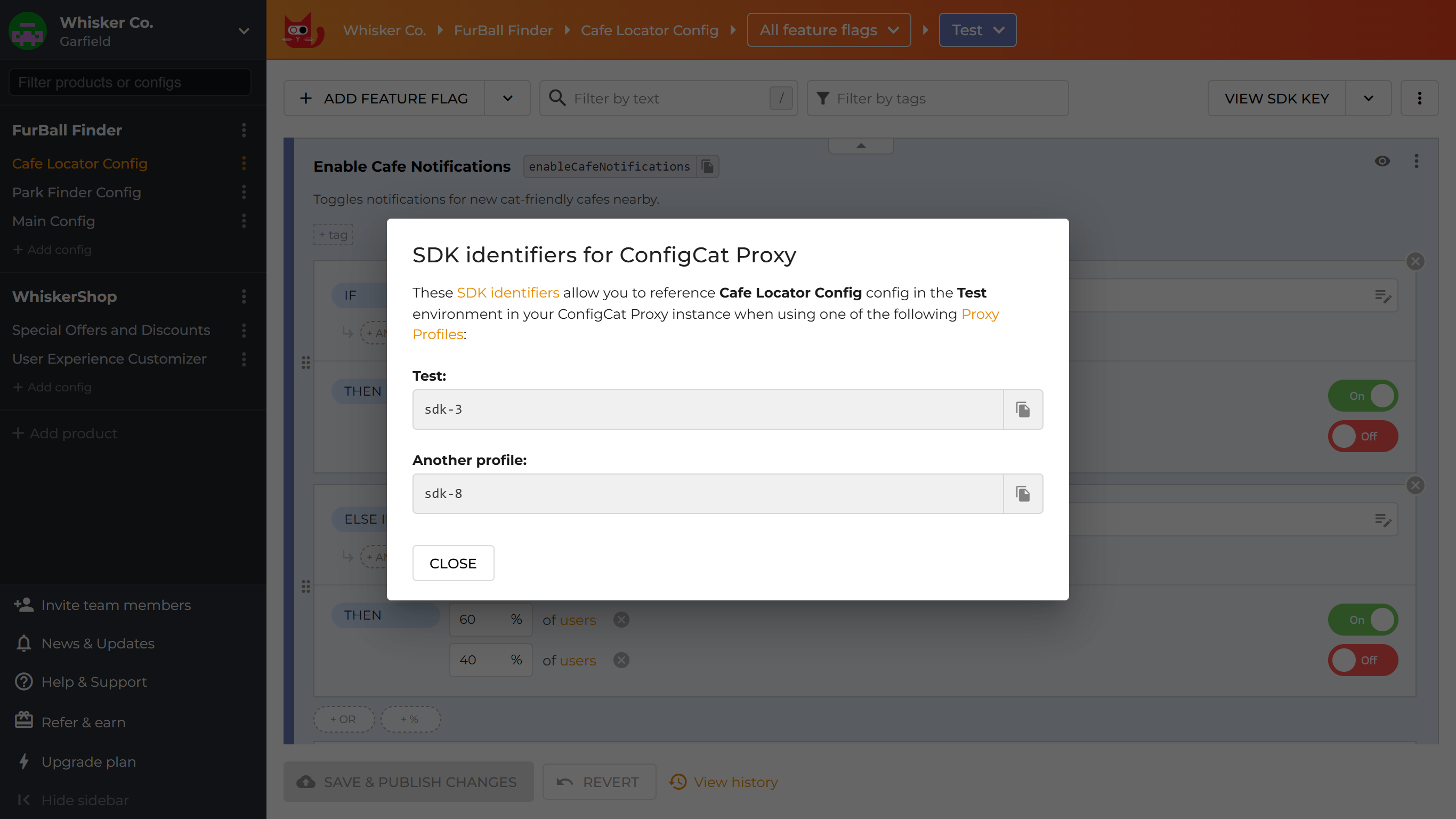
You can find the SDK identifiers generated for the selected config-environment pairs on the ConfigCat Dashboard right where you find their SDK Key.
In the dialog that appears, you can find the SDK identifiers for the current config-environment pair, listed for each available Proxy profile.
-
(Optional) Set up how your Proxy should learn about feature flag changes
There are two ways a Proxy can detect feature flag changes. Each config-environment pair identified by each SDK key is automatically monitored for changes by periodic polling of the corresponding config JSON file at a configured frequency. Besides polling, the Proxy can receive change notifications over HTTP, via its webhook endpoint.
-
Config JSON poll interval
You have the option to control how frequently the Proxy should poll for config JSON changes.
Click on the configure icon in theConnection preferencescolumn, set the poll interval and click onSAVE POLL INTERVAL.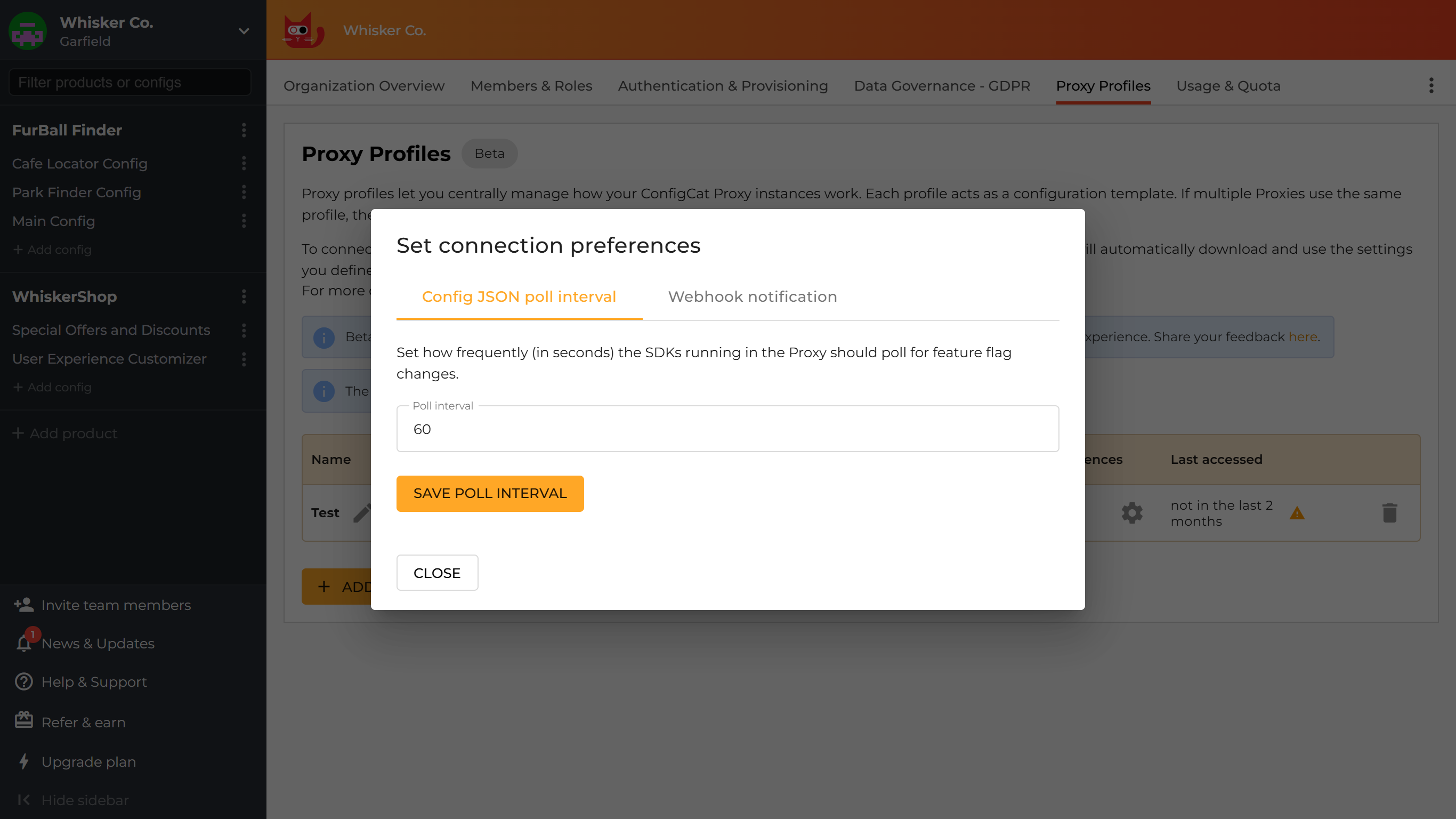
-
Webhook notification
You can set up automatic webhook notifications about feature flag changes for your Proxy by providing its public URL.
Click on the configure icon in theConnection preferencescolumn and selectWebhook notification. Then, enter your Proxy instance's public URL and clickADD PROXY URL.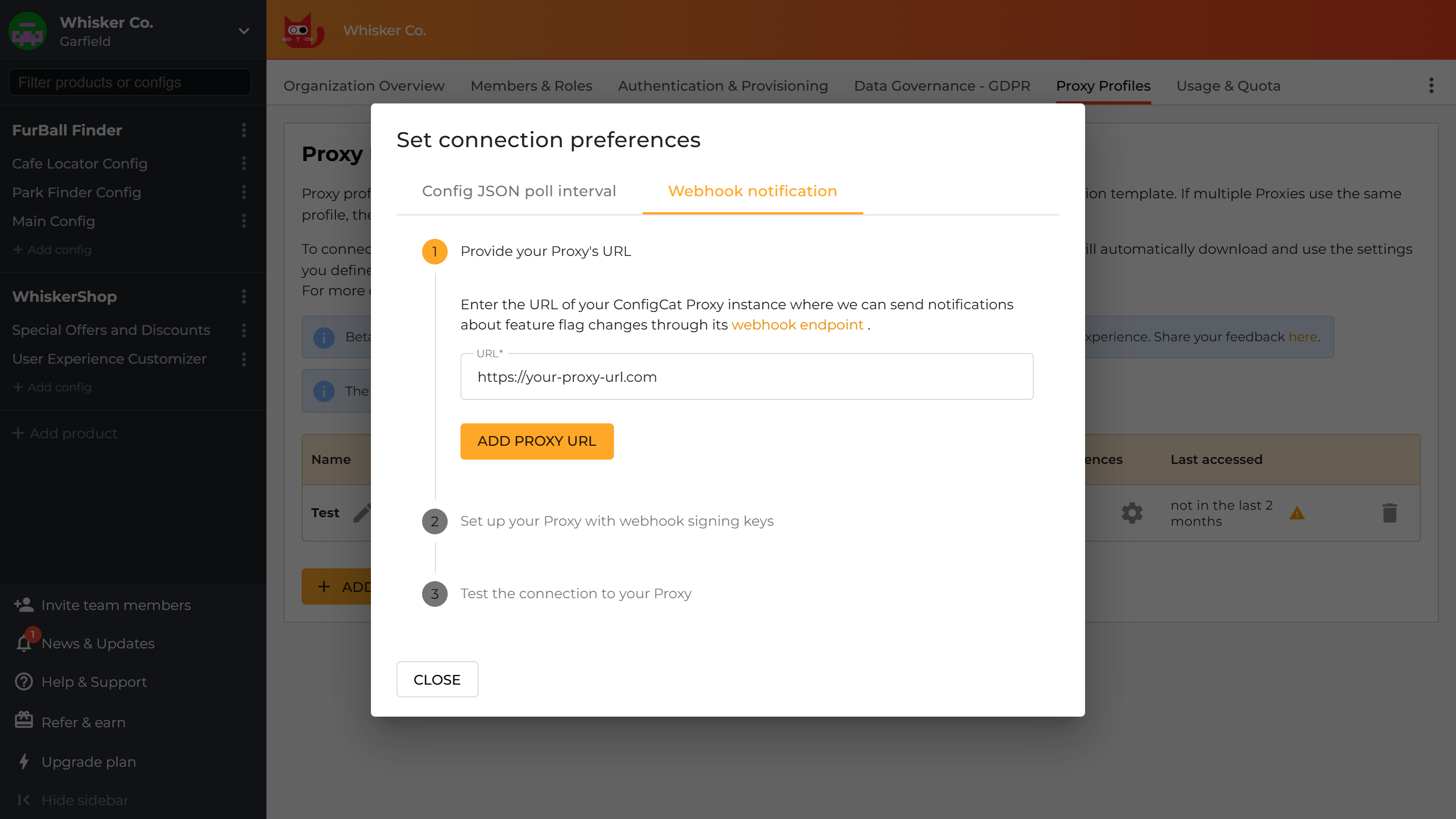
Put the displayed webhook signing key(s) into your Proxy's configuration. Signing keys are for making sure that webhook requests received by your Proxy are sent by ConfigCat. Signatures are automatically verified by the Proxy.
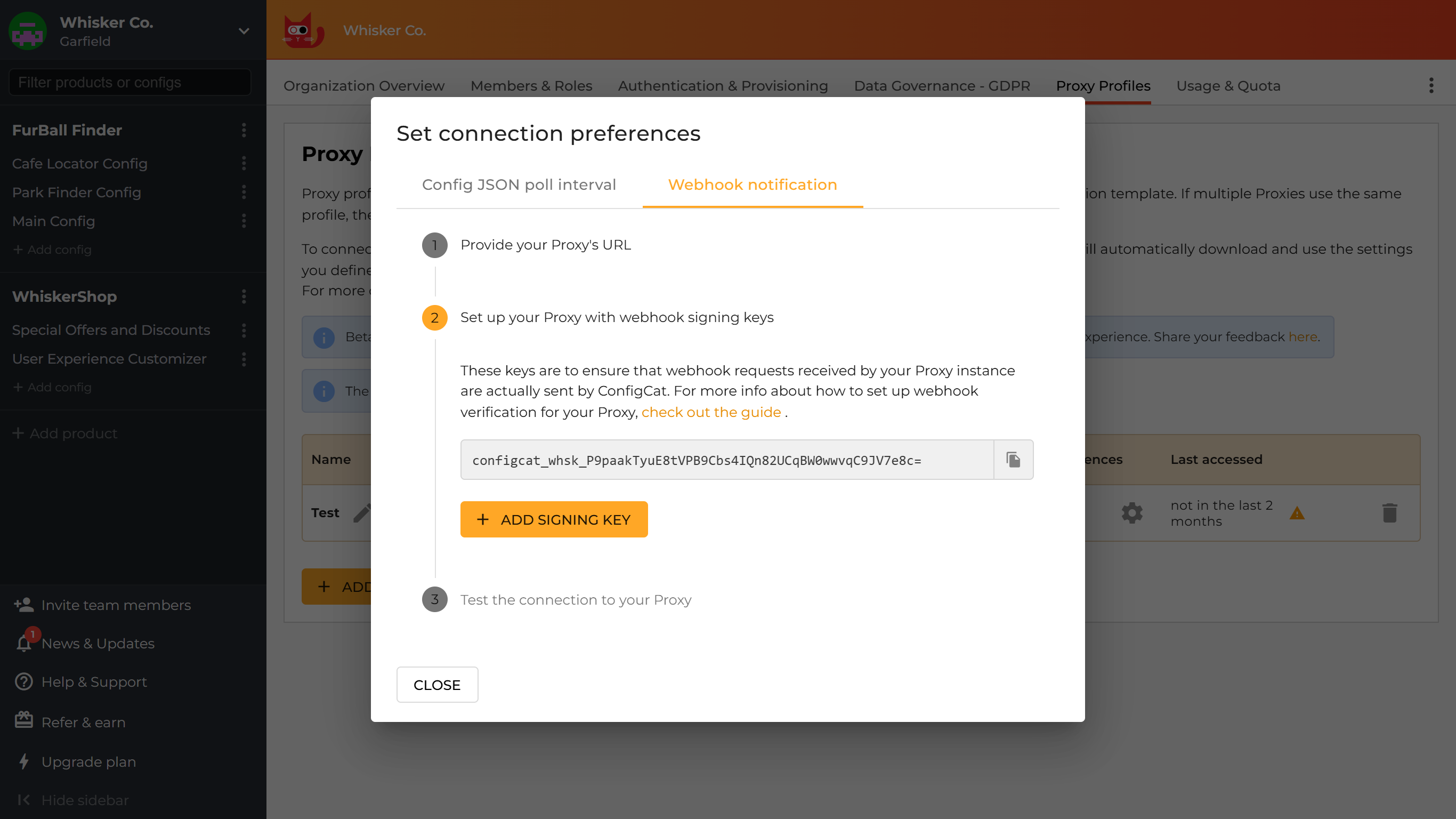
- YAML
- Environment variables
options.ymlprofile:
webhook_signing_key: <signing-key>CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_WEBHOOK_SIGNING_KEY="<signing-key>"Test the connection to your Proxy instance.
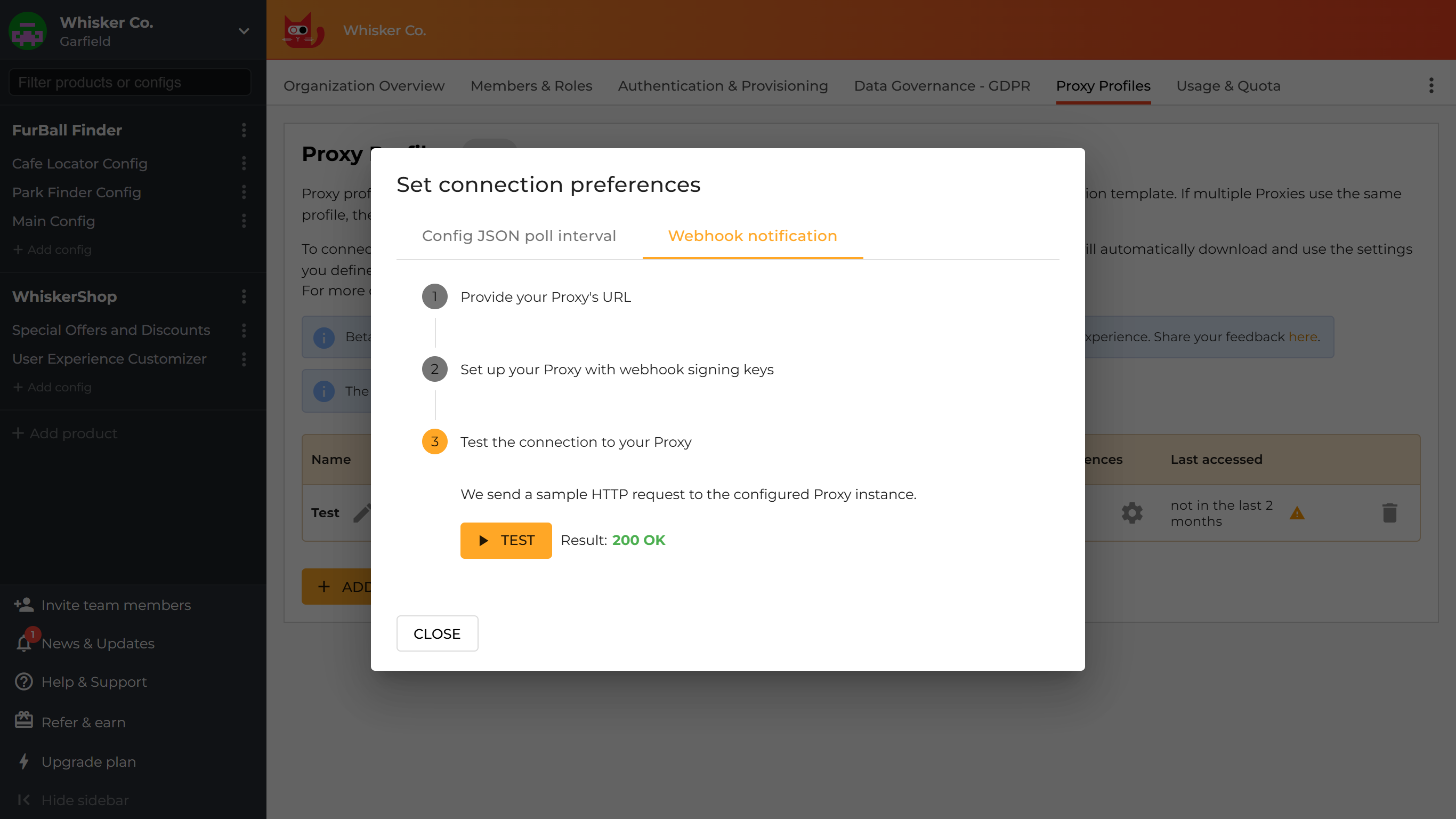
-
-
All configuration options related to Proxy profiles
Option Default Description - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
key: "<key>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_KEY="<key>"- The Proxy profile's key. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
secret: "<secret>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_SECRET="<secret>"- The Proxy profile's secret used by the Proxy to authenticate requests to the Public Management API. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
base_url: "<base-url>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_BASE_URL="<base-url>"ConfigCat Public Management API URL The base URL from where the Proxy should fetch the SDK Keys selected in the connected Proxy profile. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
poll_interval: 300CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_POLL_INTERVAL=300300 The interval (in seconds) specifying how frequently the Proxy should poll for changes in the connected Proxy profile. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
webhook_signing_key: "<signing-key>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_WEBHOOK_SIGNING_KEY="<signing-key>"- The key used to sign the webhook requests sent to the Proxy. More about how to set up webhooks for a Proxy profile. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
webhook_signature_valid_for: 300CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_WEBHOOK_SIGNATURE_VALID_FOR=300300 The time period (in seconds) within which webhook requests are considered valid. More about how to set up webhooks for a Proxy profile. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"warnThe verbosity level for Proxy profile-related logging.
Possible values:error,warn,info, ordebug.- YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
sdks:
base_url: "<sdk-base-url>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_SDKS_BASE_URL="<sdk-base-url>"ConfigCat's CDN URL. The CDN base URL (forward proxy, dedicated subscription) from where the ConfigCat SDKs should download the config JSON. - YAML
- Environment variable
profile:
sdks:
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"CONFIGCAT_PROFILE_SDKS_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"warnThe verbosity level for logging performed by the ConfigCat SDKs spawned for the connected Proxy profile.
Possible values:error,warn,info, ordebug.
Profile caching
Proxy instances running in online mode are caching their connected profile if they have a cache configured. This means that other Proxy instances running with global offline mode enabled can use those cached profiles from the same shared cache.
infoOffline Proxy instances only need the profile's
keyto read the connected profile from the cache, thesecretoption is not mandatory in this mode.
2. Manual configuration
When using environment variables, the SDK keys can be specified as a JSON object, where the property name is the SDK identifier (the identifier of the config-environment pair whose SDK Key the underlying SDK instance is configured to use) and the property value is the actual SDK key. The SDK identifier part is later used in endpoint routes to recognize which SDK must serve the given flag evaluation request.
Furthermore, when configuring the Proxy via environment variables, the identifier becomes a part of the SDK specific environment variable's name in the following format: CONFIGCAT_<SDK_ID>_<OPTION>.
For example, suppose we have the following setup: CONFIGCAT_SDKS={"my_sdk":"<your-sdk-key>"}.
In this case, the environment variable that sets the corresponding SDK instance's poll interval will be named as follows: CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_POLL_INTERVAL.
The SDK identifier part of the environment variables is always transformed to uppercase and each hyphen (-) character is replaced with underscore (_).
In case of a YAML file, the SDK identifier is the property name set under the sdks node.
sdks:
my_sdk:
...
- YAML
- Environment variables
This is the whole YAML section of the SDK specific options.
sdks:
my_sdk:
key: "<your-sdk-key>"
base_url: "<base-url>"
poll_interval: 60
data_governance: <"eu"|"global">
webhook_signing_key: "<key>"
webhook_signature_valid_for: 300
default_user_attributes:
attribute_key: "<attribute_value>"
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"
offline:
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"
enabled: <true|false>
use_cache: <true|false>
cache_poll_interval: 5
local:
file_path: "./path/local.json"
polling: <true|false>
poll_interval: 5
another_sdk:
...
These are the SDK specific environment variables.
CONFIGCAT_SDKS='{"my_sdk":"<your-sdk-key>","another-sdk":"<another-sdk-key>"}'
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_BASE_URL="<base-url>"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_POLL_INTERVAL=30
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_DATA_GOVERNANCE="<eu|global>"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_LOCAL_FILE_PATH="./path/local.json"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_LOCAL_POLLING=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_LOCAL_POLL_INTERVAL=5
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_USE_CACHE=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_OFFLINE_CACHE_POLL_INTERVAL=5
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_WEBHOOK_SIGNING_KEY="<key>"
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_WEBHOOK_SIGNATURE_VALID_FOR=300
CONFIGCAT_MY_SDK_DEFAULT_USER_ATTRIBUTES='{"attribute_key":"<attribute_value>"}'
CONFIGCAT_ANOTHER_SDK_POLL_INTERVAL=15
...
Here's the explanation for each option:
SDK Identifier / SDK Key mapping
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| The SDK identifier and the associated SDK key. |
Additional options for underlying SDKs
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ConfigCat's CDN URL. | The CDN base URL (forward proxy, dedicated subscription) from where the SDK should download the config JSON. |
| 60 | The underlying SDK's polling interval in seconds. |
| global | Describes the location of your feature flag and setting data within the ConfigCat CDN. This parameter needs to be in sync with your Data Governance preferences. More about Data Governance. |
| - | The key used to sign the webhook requests sent to the Proxy. More about the webhook endpoint. |
| 300 | The time period (in seconds) within which webhook requests are considered valid. More about the webhook endpoint. |
| - | Additional SDK specific default user attributes. The Proxy will use these attributes when an evaluation request doesn't contain a value for the predefined attribute. When there's a default value defined for the same attribute at both SDK and global level, the one at the SDK level will take precedence. |
| warn | The verbosity level for logging performed by the underlying SDK. Possible values: error, warn, info, or debug. |
Offline Mode
The following options are specific to the SDK's offline mode. In offline mode, there are two ways the Proxy can provide the underlying SDKs with the data required for feature flag evaluation.
- Polling a cache: The Proxy can poll a cache for feature flag changes. It can use a shared cache that an online Proxy instance writes to. More about the cache option.
- Watching / polling a file: The Proxy can watch or poll for modifications in a file that contains data for feature flag evaluation. For watching, the Proxy uses the fsnotify library.
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns the SDK's offline mode on/off. In offline mode, the SDK will not communicate with the ConfigCat CDN network. Instead, it uses the configured cache or a file as the source of its config JSON. |
| false | Controls whether the SDK should use the configured cache as the source of its config JSON. More about the cache option. |
| 5 | The cache polling interval in seconds. Used only, when the use_cache option is true. More about the cache option. |
| warn | The verbosity level for offline mode-related logging. Possible values: error, warn, info or debug. |
| - | Path to the local file that contains the config JSON to use for feature flag evaluation. |
| false | Controls whether the Proxy should use polling instead of file system watching for monitoring the local file for changes. |
| 5 | The interval to use for polling the local file in seconds. |
Default User Attributes
There's an option to predefine User Object attributes with default values. Whenever the Proxy receives an evaluation request, it will automatically attach these predefined attributes to the request. If the evaluation request contains a different value for an attribute you previously defined, the request's value will take precedence.
- YAML
- Environment variables
default_user_attributes:
attribute_key1: "<attribute_value1>"
attribute_key2: "<attribute_value2>"
CONFIGCAT_DEFAULT_USER_ATTRIBUTES='{"attribute_key1":"<attribute_value1>","attribute_key2":"<attribute_value2>"}'
It's also possible to set default user attributes at the SDK level. See the SDK options section above for more details.
Global Offline Mode
It is possible to turn on offline mode globally for a whole Proxy instance. When it's turned on, each underlying SDK switches to work from the configured cache.
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns the global offline mode on/off. |
| 5 | The cache polling interval in seconds. More about the cache option. |
| warn | The verbosity of the offline mode related logs. Possible values: error, warn, info or debug. |
When an SDK also has its offline option set, that will override what it would inherit from the global offline option.
Cache
The Proxy in its default setup stores all the information it needs for feature flag evaluation in memory. This behavior is extendable with an external cache that you can use for pointing the underlying SDKs to your own data storage.
Currently, Redis, MongoDB, and DynamoDB is supported as external cache. The cache key for the underlying SDKs is based on the SDK Key. This means that multiple Proxy instances using the same SDK key will read/write the same cache entry.
The ConfigCat Proxy supports shared caching, which means it can feed an external cache that is shared by other ConfigCat SDKs. You can read more about this feature and the required minimum SDK versions here.
Redis
- YAML
- Environment variables
This is the whole YAML section of the Redis specific options.
cache:
redis:
enabled: <true|false>
db: 0
user: "<user>"
password: "<pass>"
addresses: ["<addr1>", "<addr2>"]
tls:
enabled: <true|false>
min_version: <1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
server_name: "<server-name>"
certificates:
- cert: "<path-to-cert>"
key: "<path-to-key>"
These are the Redis specific environment variables.
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_DB=0
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_USER="<user>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_PASSWORD="<pass>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_ADDRESSES='["<addr1>", "<addr2>"]'
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_TLS_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_TLS_MIN_VERSION=<1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_TLS_SERVER_NAME="<server-name>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_REDIS_TLS_CERTIFICATES='[{"key":"<path-to-key>","cert":"<path-to-cert>"}]'
Here's the explanation for each option:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns caching into Redis on/off. |
| ["localhost:6379"] | The addresses of the Redis instances. The Proxy uses Universal Redis clients, so if the array contains multiple addresses, it will use a ClusterClient instance. |
| 0 | The selected Redis database. |
| - | The username for connecting to Redis. |
| - | The password for connecting to Redis. |
The following options are for securing the connection to Redis with TLS.
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns the TLS connection to Redis on/off. |
| 1.2 | The minimum TLS version to use. |
| - | The name of the Redis server. |
| - | A list of TLS certificate/key pairs. |
MongoDB
When the configured MongoDB database and collection doesn't exist, the Proxy automatically creates them. The following document structure is used to store the downloaded config JSON in BSON format:
{
"key": "<The unique cache key determined by the ConfigCat SDK within the Proxy>",
"payload": "<The downloaded config JSON in a standardized format determined by the ConfigCat SDK within the Proxy>"
}
At the collection creation, the Proxy also creates a unique index for the key field.
- YAML
- Environment variables
This is the whole YAML section of the MongoDB specific options.
cache:
mongodb:
enabled: <true|false>
url: "<connection-url>"
database: "<database-name>"
collection: "<collection-name>"
tls:
enabled: <true|false>
min_version: <1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
server_name: "<server-name>"
certificates:
- cert: "<path-to-cert>"
key: "<path-to-key>"
These are the MongoDB specific environment variables.
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_URL="<connection-url>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_DATABASE="<database-name>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_COLLECTION="<collection-name>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_TLS_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_TLS_MIN_VERSION=<1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_TLS_SERVER_NAME="<server-name>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_MONGODB_TLS_CERTIFICATES='[{"key":"<path-to-key>","cert":"<path-to-cert>"}]'
Here's the explanation for each option:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns caching into MongoDB on/off. |
| - | The connection url to MongoDB. |
| configcat_proxy | The name of the MongoDB database that the Proxy will use for storing data. |
| cache | The name of the collection inside the MongoDB database. |
The following options are for securing the connection to MongoDB with TLS.
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns the TLS connection to MongoDB on/off. |
| 1.2 | The minimum TLS version to use. |
| - | The name of the MongoDB server. |
| - | A list of TLS certificate/key pairs. |
DynamoDB
By default, the Proxy uses the standard AWS CLI environment variables (or a local AWS configuration file) to read the AWS credentials and region for connecting to DynamoDB.
The Proxy doesn't create the DynamoDB table automatically, it must already exist with a partition key called key. The data stored in the table has the following attributes:
key: The unique cache key determined by the ConfigCat SDK within the Proxy.payload: The downloaded config JSON in a standardized format determined by the ConfigCat SDK within the Proxy.
The following permissions are needed to read and write the table:
GetItemPutItem
- YAML
- Environment variables
This is the whole YAML section of the DynamoDB specific options.
cache:
dynamodb:
enabled: <true|false>
url: "<url>"
table: "<table-name>"
These are the DynamoDB specific environment variables.
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_DYNAMODB_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_DYNAMODB_URL="<url>"
CONFIGCAT_CACHE_DYNAMODB_TABLE="<table-name>"
Here's the explanation for each option:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns caching into DynamoDB on/off. |
| - | The DynamoDB service endpoint. |
| configcat_proxy_cache | The name of the DynamoDB table that the Proxy will use for storing data. |
HTTP
The following HTTP and HTTP Proxy related options are available:
- YAML
- Environment variables
http:
enabled: <true|false>
port: 8050
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"
status:
enabled: <true|false>
http_proxy:
url: "<proxy-url>"
CONFIGCAT_HTTP_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_HTTP_PORT=8050
CONFIGCAT_HTTP_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"
CONFIGCAT_HTTP_STATUS_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_HTTP_PROXY_URL="<proxy-url>"
Here's the explanation for each option:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| true | Turns the main HTTP server on/off. This server hosts the CDN proxy, API, SSE, and webhook endpoints. |
| 8050 | The main HTTP server's port. |
| warn | The verbosity of the HTTP related logs. Possible values: error, warn, info, or debug.When debug is set, the Proxy will log each HTTP request with additional details. |
| false | Turns the hosting of the status endpoint on the main HTTP port (default: 8050) on/off. |
HTTP Proxy
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| - | The network proxy's URL that the ConfigCat Proxy must use for communication through the internet. |
Endpoints
The options for HTTP endpoints are discussed in the Endpoints section.
TLS
For securing direct communication to the ConfigCat Proxy, you have the option to set up TLS. Another option would be to use a full-featured reverse proxy that secures the communication and forwards each request to the Proxy.
The following options are for the first scenario where you secure the direct HTTP and gRPC communication.
- YAML
- Environment variables
tls:
enabled: <true|false>
min_version: <1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
certificates:
- cert: "<path-to-cert>"
key: "<path-to-key>"
CONFIGCAT_TLS_ENABLED=<true|false>
CONFIGCAT_TLS_MIN_VERSION=<1.0|1.1|1.2|1.3>
CONFIGCAT_TLS_CERTIFICATES='[{"key":"<path-to-key>","cert":"<path-to-cert>"}]'
Here's the explanation for each option:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| false | Turns the enforcement of TLS connection to the ConfigCat Proxy on/off. |
| 1.2 | The minimum TLS version to accept. |
| - | A list of TLS certificate/key pairs. |
Logging
The Proxy supports the following log levels: debug, info, warn, and error. The default is warn.
You can specify the log level either globally or for each individual component. If you don't set a component's log level explicitly, it will inherit the global level's value.
- YAML
- Environment variables
log:
level: "<error|warn|info|debug>"
CONFIGCAT_LOG_LEVEL="<error|warn|info|debug>"
When the main HTTP server's or gRPC server's log level is set to debug, each HTTP request or RPC the Proxy receives is logged with additional details. (duration, response status, etc.)