Scan & Upload Code References Overview
ConfigCat's CLI has the ability to scan your source code for feature flag and setting usages and upload the found code references to ConfigCat.
This feature makes the elimination of the technical debt easier, as it can show which repositories reference your feature flags and settings in one centralized place on your Dashboard.
You can integrate the CLI into your CI/CD pipeline or use it with other execution mechanisms like scheduled jobs or VCS push triggered workflows.
Scan
The following example shows a simple scan execution that prints the scan result to the console. The scan command searches for every feature flag and setting key defined within a selected Config.
If you want to see this in action on your project, run the following command in its root folder:
configcat scan . --print
See the scan command's reference documentation for all available command parameters.
Deleted Flags
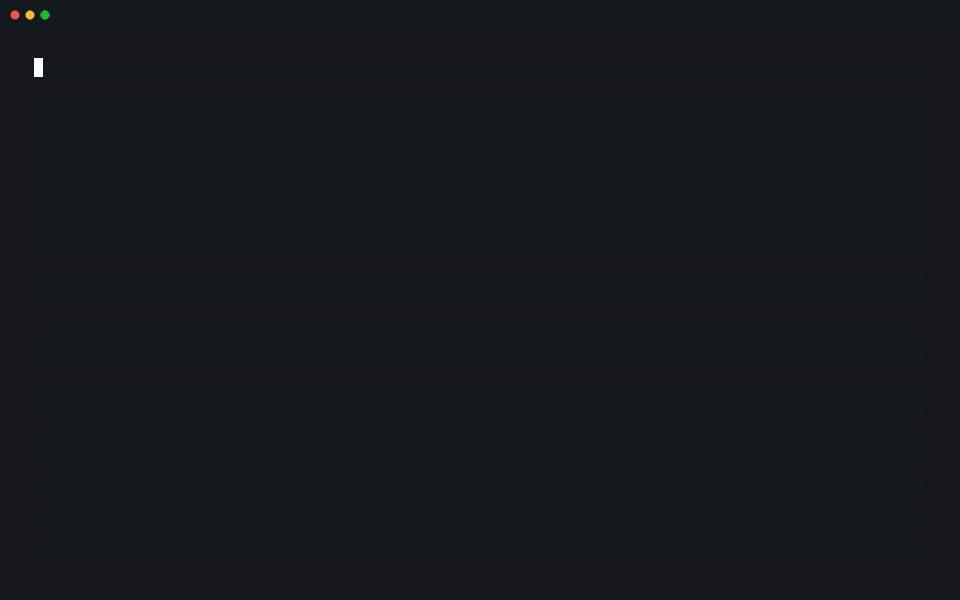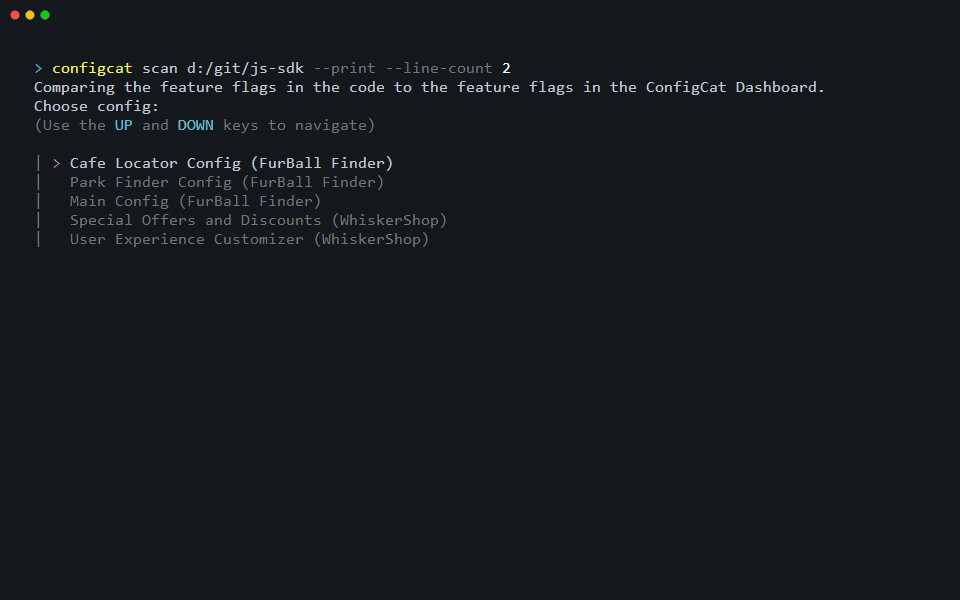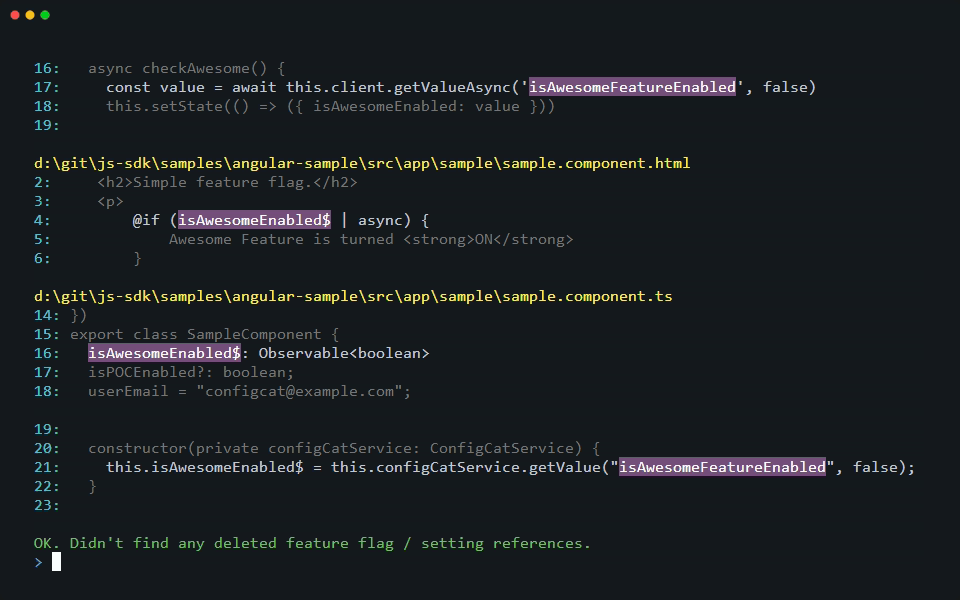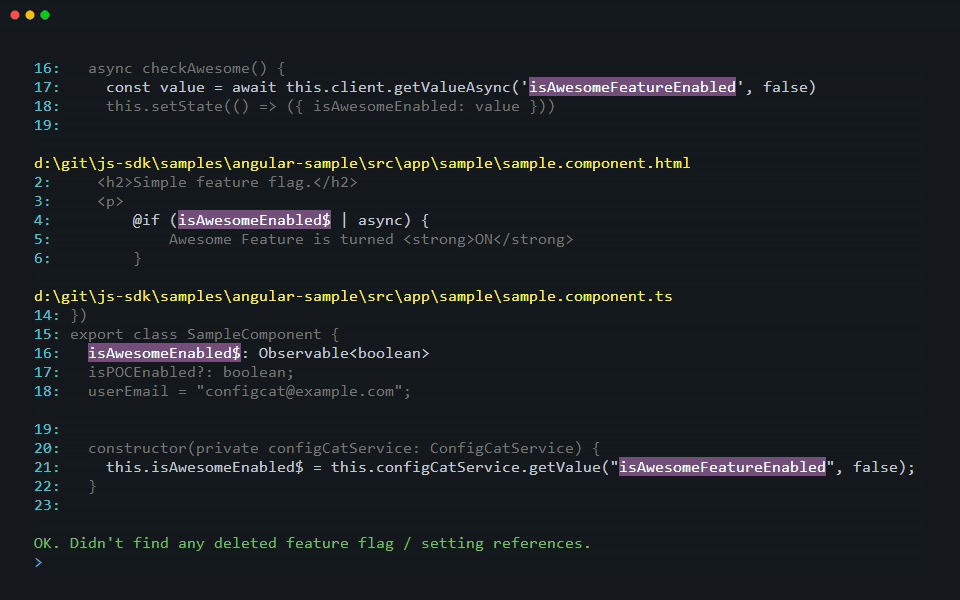
As part of the scanning operation, the CLI gathers all deleted feature flags and settings from the last 180 days and looks for their usage in your source code. When it finds a reference to a deleted feature flag or setting, it prints a warning that lists their keys.
[warning]: 5 deleted feature flag/setting reference(s) found in 4 file(s). Keys: [featureThatWasDeleted1, featureThatWasDeleted2]
Exclude Flags from Scanning
There's an option to exclude feature flags or settings from the scanning operation by their keys.
configcat scan <dir> --exclude-flag-keys featureFlagToExclude1 featureFlagToExclude2
Config ID
In non-interactive environments, like in a CI/CD pipeline, you have to pass the ID of your ConfigCat Config that you want to scan against. The scanner will use this ID to determine which feature flags & settings to search for in your source code.
To get the ID of a Config, follow the steps below:
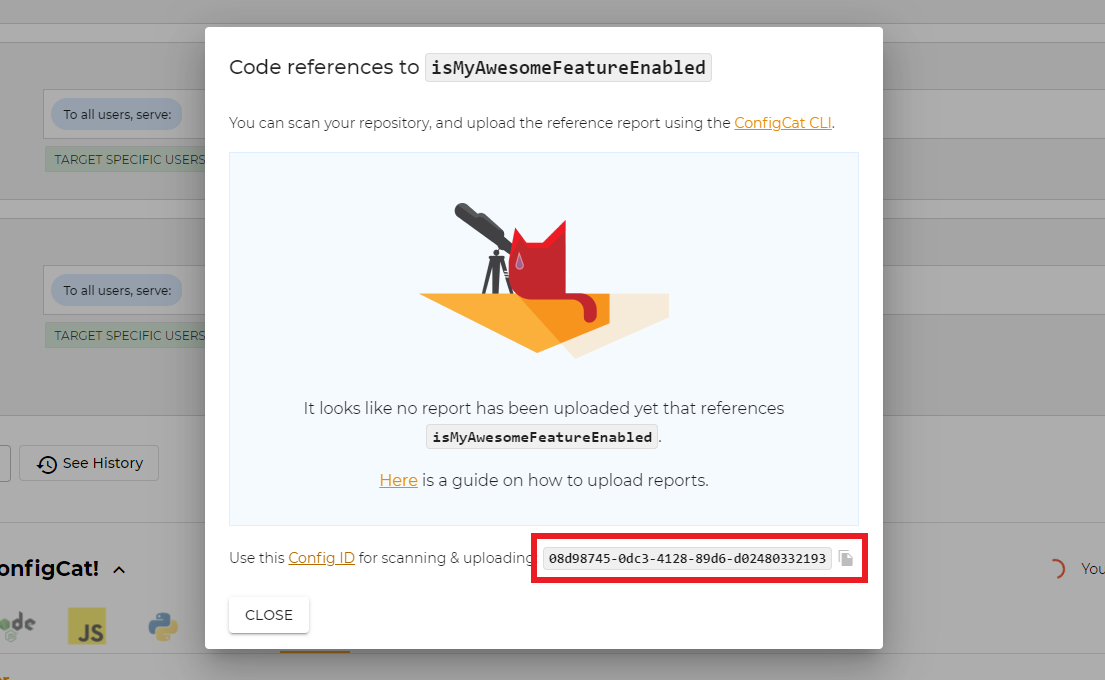
- Go to your ConfigCat Dashboard, select the desired Config, and click the code references icon on one of your feature flags.
- Copy the Config ID from the highlighted box.
How Scanning Works
The scanner looks for feature flag and setting keys between quotation marks (' " `) in the first place.
There's an option to extend the feature flag and setting key usage regex patterns with the --usage-patterns argument of the scan command.
configcat scan <dir> --usage-patterns "<pattern1>" "<pattern2>"
Usage patterns can also be set via the CONFIGCAT_USAGE_PATTERNS environment variable as a comma delimited list.
export CONFIGCAT_USAGE_PATTERNS="<pattern1>,<pattern2>";
The regex pattern must include the CC_KEY placeholder that represents the actual feature flag or setting key in your code.
For example, the following pattern allows the recognition of Ruby symbols as flag key usages:
configcat scan <dir> --usage-patterns ":CC_KEY"
It will match the following usage:
if FeatureFlags.enabled(:my_feature_key)
#...
end
Aliases
The found keys' context is examined for aliases, like variables, constants, or enumerations used to store these keys. Aliases are treated as indirect references and are included in the searching process.
For example, the following C# constant's name (MyAwesomeFeature) will be recognized as an alias:
public static class FeatureFlagKeys
{
public const string MyAwesomeFeature = "my_awesome_feature";
}
The scanner will treat this constant's usage as an indirect reference to the flag.
if (await configCatClient.GetValueAsync(FeatureFlagKeys.MyAwesomeFeature, false))
{
// the feature is on.
}
The alias recognition adapts to the characteristics of different languages.
For example, it can find aliases in Go constants/variable assignments:
const (
myAwesomeFeature string = "my_awesome_feature"
)
myAwesomeFeature := "my_awesome_feature"
And in Swift enums/variable assignments as well:
enum FlagKeys : String {
case MyAwesomeFeature = "my_awesome_feature"
}
let myAwesomeFeature: String = "my_awesome_feature"
You can check here a bunch of other samples that we tested.
An alias must be at least 30% identical to the feature flag/setting key.
The similarity check is case insensitive and ignores _ characters.
This behavior prevents false recognitions in expressions like <input type="text" value="my_awesome_feature"> where value shouldn't be treated as alias.
Custom alias match patterns
There's an option to set custom regex patterns for identifying additional aliases. The scan command accepts a list of patterns via the --alias-patterns argument.
configcat scan <dir> --alias-patterns "<pattern1>" "<pattern2>"
The CLI also accepts patterns from the CONFIGCAT_ALIAS_PATTERNS environment variable as a comma delimited list.
export CONFIGCAT_ALIAS_PATTERNS="<pattern1>,<pattern2>";
Match pattern format
The regex pattern must include at least one capture group that represents the actual alias. When more than one group is defined, the first one is selected.
To bind the actual flag keys to aliases, the CLI uses a CC_KEY placeholder to inject the known keys into the pattern.
For example, the following pattern allows to find aliases that point to Ruby symbols:
configcat scan <dir> --alias-patterns "(\w+) = client\.get_value\(:CC_KEY"
It will match to the following usage:
# 'my_feature_enabled' is now treated as an alias to the 'my_feature_key' flag.
my_feature_enabled = client.get_value(:my_feature_key, false)
The CLI implicitly adds the optional `, ', " wrapping around flag keys, so you don't have to wrap the CC_KEY placeholder manually.
For example, the pattern (\w+) = CC_KEY will either match to alias = flag_key, alias = "flag_key", alias = 'flag_key', or alias = `flag_key` .
Wrappers
In addition to aliases, the scanner also looks for different feature flag/setting key usage patterns. This helps to recognize functions and properties used to wrap direct ConfigCat SDK calls as indirect references. Aliases are also included in this search.
For example, the scanner will treat the IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled function of the following C# wrapper class as an indirect reference:
public class FeatureFlagProvider
{
public async Task<bool> IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled(bool defaultValue = false)
{
return await configCatClient.GetValueAsync("my_awesome_feature", defaultValue);
}
}
And will include its usage in the scan report:
if (await featureFlagProvider.IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled())
{
// the feature is on.
}
The scanner uses the following patterns to look for wrapper usages (case insensitive):
[.|->|::]{settingKeyOrAlias}[.|->|::]get{settingKeyOrAlias}[.|->|::]is{settingKeyOrAlias}[.|->|::]is{settingKeyOrAlias}enabled
Given the key/alias my_awesome_feature, the scanner will find any of the following usage examples:
.my_awesome_feature(also:->my_awesome_feature/::my_awesome_feature).MY_AWESOME_FEATURE(also:->MY_AWESOME_FEATURE/::MY_AWESOME_FEATURE).get_my_awesome_feature(also:->get_my_awesome_feature/::get_my_awesome_feature).GET_MY_AWESOME_FEATURE(also:->GET_MY_AWESOME_FEATURE/::GET_MY_AWESOME_FEATURE).is_my_awesome_feature(also:->is_my_awesome_feature/::is_my_awesome_feature).is_my_awesome_feature_enabled(also:->is_my_awesome_feature_enabled/::is_my_awesome_feature_enabled).myAwesomeFeature(also:->myAwesomeFeature/::myAwesomeFeature).getMyAwesomeFeature(also:->getMyAwesomeFeature/::getMyAwesomeFeature).isMyAwesomeFeature(also:->isMyAwesomeFeature/::isMyAwesomeFeature).isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled(also:->isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled/::isMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled).IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled(also:->IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled/::IsMyAwesomeFeatureEnabled)
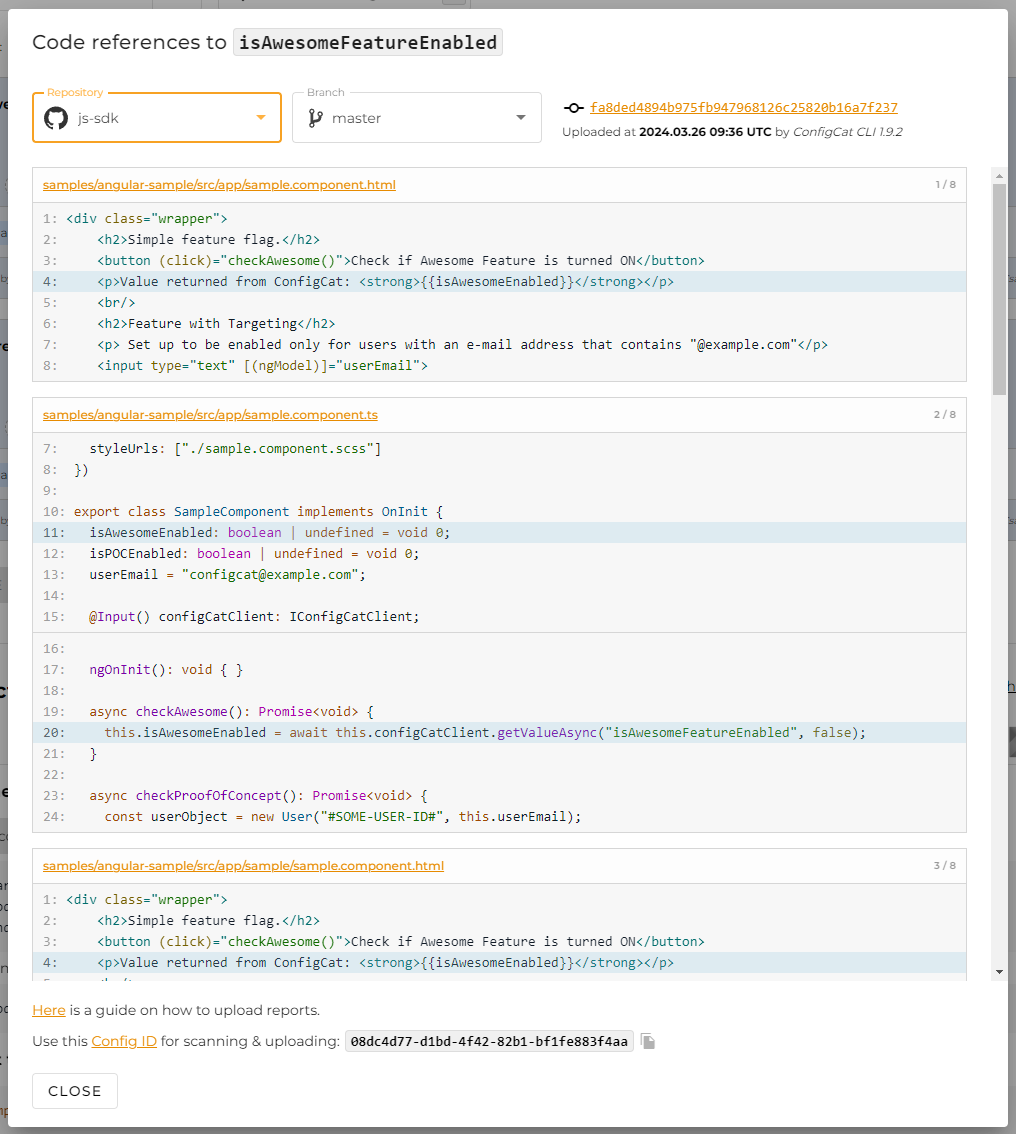
Upload Scan Reports
You have the option to upload scan reports for each branch of your repository to ConfigCat. Each scan report is associated to one of these branches.
The following screenshot shows how an uploaded report looks like.
Scanning Git Repositories
The scan command automatically detects when it's being executed on a git repository. It collects additional information from Git like the current branch
name, the actual commit hash, and each active remote branch. These extra details are used to enrich the uploaded report on the ConfigCat Dashboard with links to your actual source code.
If you are not using Git as VCS, you have to set at least the --branch parameter of the scan command.
Template URLs
The scan command's --file-url-template and --commit-url-template parameters are used for generating links to your repository.
Based on the information available during the scanning, the CLI replaces the corresponding template parameters to generate the actual links.
-
File URL template: Used to generate VCS file links.
Available template parameters:commitHashfilePathlineNumber
With the following example template URL:
https://github.com/my/repo/blob/{commitHash}/{filePath}#L{lineNumber}
For the filesrc/example.js, the result is:https://github.com/my/repo/blob/4451d61b63a4b4499ed5c607be6c40ce9eeadb9c/src/example.js#L69 -
Commit URL template: Used to generate VCS commit links.
Available template parameters:commitHash
With the following example template URL:
https://github.com/my/repo/commit/{commitHash}
For the commit hash4451d61b63a4b4499ed5c607be6c40ce9eeadb9c, the result is:https://github.com/my/repo/commit/4451d61b63a4b4499ed5c607be6c40ce9eeadb9c
When these template URLs are not set, the uploaded report will not contain VCS links.
Stale Branches
When the scan is executed on a Git repository, the CLI attaches the currently active remote branches to the uploaded report. This information is used for cleaning up each stale report that belongs to a deleted branch.
CI/CD Integrations
We prepared the following integrations to simplify the usage of the scanner in your CI/CD workflow:
Manual Integration
If your workflow doesn't have an integration, you can follow the instructions here to set scan executions directly with the ConfigCat CLI.
Ignore Files
The scan command respects all include and exclude patterns listed inside .gitignore and .ignore files within the scanned directory.
In addition, you can create an extra .ccignore file with patterns that the scanner must take into account.
Each pattern must follow the gitignore pattern format.